Simple Generative Adversarial Network to generate datapoints from a simple one-dimensional function
(adapted from https://machinelearningmastery.com/how-to-develop-a-generative-adversarial-network-for-a-1-dimensional-function-from-scratch-in-keras/).
from keras.models import Sequential
from keras.layers import Dense
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from numpy import zeros
from numpy import ones
import numpy as np
from numpy import hstack
from numpy.random import rand
from numpy.random import randn
from keras.initializers import RandomNormal
from keras.models import Input
from keras.models import Model
from keras.utils.vis_utils import plot_model
Using TensorFlow backend.
Simple Discriminator
def build_discriminator(input_shape):
model_input = Input(shape=input_shape)
dense = Dense(20, activation='relu', kernel_initializer=RandomNormal(stddev=0.02))(model_input)
model_output = Dense(1,activation='sigmoid')(dense)
model = Model(model_input, model_output)
model.compile(loss='binary_crossentropy', optimizer='adam', metrics=['accuracy'])
return model
#Test the discriminator model
input_shape = (2,) #our input data will be 2-dimensional (x1,x2)
model = build_discriminator(input_shape)
# summarize the model
model.summary()
del model
_________________________________________________________________
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
=================================================================
input_1 (InputLayer) (None, 2) 0
_________________________________________________________________
dense_1 (Dense) (None, 20) 60
_________________________________________________________________
dense_2 (Dense) (None, 1) 21
=================================================================
Total params: 81
Trainable params: 81
Non-trainable params: 0
_________________________________________________________________
Simple generator
# generate inputs for the generator
def generate_latent_points(latent_dim, n):
# generate points in the latent space
x_input = randn(latent_dim * n)
# reshape into a batch of inputs for the network
x_input = x_input.reshape(n, latent_dim)
return x_input
def build_generator(input_shape,output_shape):
model_input = Input(shape=input_shape)
dense = Dense(20, activation='relu', kernel_initializer='he_uniform')(model_input)
model_output = Dense(output_shape[0], activation='linear')(dense)
model = Model(model_input, model_output)
return model
#Test the generator model
input_shape = (5,)
output_shape = (2,)
model = build_generator(input_shape,output_shape)
model.summary()
del model
_________________________________________________________________
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
=================================================================
input_2 (InputLayer) (None, 5) 0
_________________________________________________________________
dense_3 (Dense) (None, 20) 120
_________________________________________________________________
dense_4 (Dense) (None, 2) 42
=================================================================
Total params: 162
Trainable params: 162
Non-trainable params: 0
_________________________________________________________________
# Combine generator and discriminator into a gan model, this will update the generator
def build_gan(generator, discriminator, input_shape):
# freeze the discriminator, make its weights non-trainable
discriminator.trainable = False
model_input = Input(shape=input_shape)
generator_output = generator(model_input)
discriminator_output = discriminator(generator_output)
gan_model = Model(model_input, discriminator_output)
gan_model.compile(loss='binary_crossentropy', optimizer='adam')
return gan_model
Create the discriminator, generator and GAN
# size of the latent space
latent_dim = 5
# create the discriminator
input_shape = (2,)
discriminator_model = build_discriminator(input_shape)
# create the generator
input_shape = (latent_dim,)
output_shape = (2,)
generator_model = build_generator(input_shape,output_shape)
# create the gan model connecting the generator and the discriminator
gan_model = build_gan(generator_model, discriminator_model,input_shape)
Generate some real and fake data
import math
import numpy as np
# generate n real samples with 1 as class labels
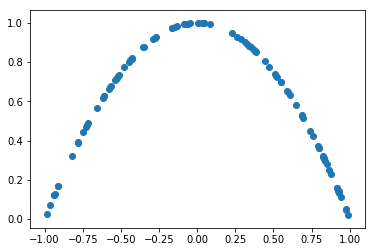
def generate_real_samples(n):
# generate inputs in [-0.5, 0.5]
X1 = np.random.uniform(-1,1,n)
# generate outputs X^2
X2 = 1 - X1**2
# stack arrays
X1 = X1.reshape(n, 1)
X2 = X2.reshape(n, 1)
X = hstack((X1, X2))
# generate class labels
y = ones((n, 1))
return X, y
X,y = generate_real_samples(100)
plt.scatter(X[:,0],X[:,1])
<matplotlib.collections.PathCollection at 0x7efd39eb7e10>
# generate n fake samples with 0 as class labels
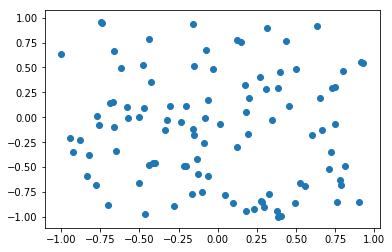
def generate_fake_samples(n):
# generate inputs in [-1, 1]
X1 = -1 + rand(n) * 2
# generate outputs in [-1, 1]
X2 = -1 + rand(n) * 2
# stack arrays
X1 = X1.reshape(n, 1)
X2 = X2.reshape(n, 1)
X = hstack((X1, X2))
# generate class labels
y = zeros((n, 1))
return X, y
X,y = generate_fake_samples(100)
plt.scatter(X[:,0],X[:,1])
<matplotlib.collections.PathCollection at 0x7efd39e634a8>
Do some training
# evaluate the discriminator and plot real and fake points
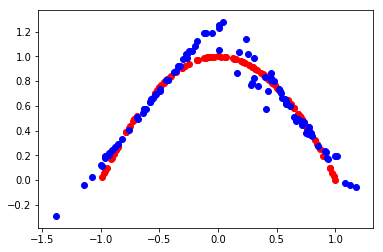
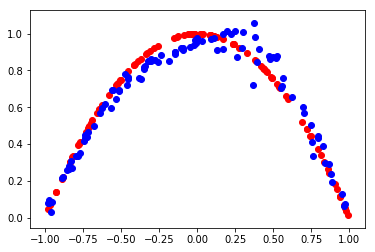
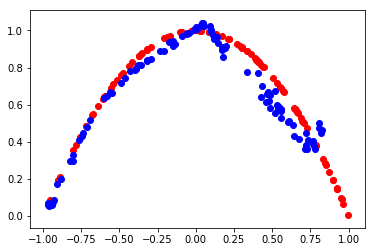
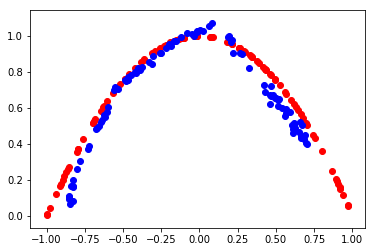
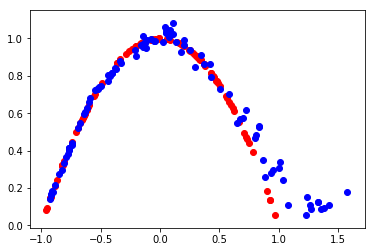
def evaluate(epoch, generator, discriminator, latent_dim, n=100):
# prepare real samples
x_real, y_real = generate_real_samples(n)
# evaluate discriminator on real examples
_, acc_real = discriminator.evaluate(x_real, y_real, verbose=0)
# prepare fake examples
x_input = generate_latent_points(latent_dim, n)
# predict outputs
x_fake = generator.predict(generate_latent_points(latent_dim, n))
# create class labels
y_fake = zeros((n, 1))
# evaluate discriminator on fake examples
_, acc_fake = discriminator.evaluate(x_fake, y_fake, verbose=0)
# summarize discriminator performance
print(epoch, acc_real, acc_fake)
# scatter plot real and fake data points
plt.scatter(x_real[:, 0], x_real[:, 1], color='red')
plt.scatter(x_fake[:, 0], x_fake[:, 1], color='blue')
plt.show()
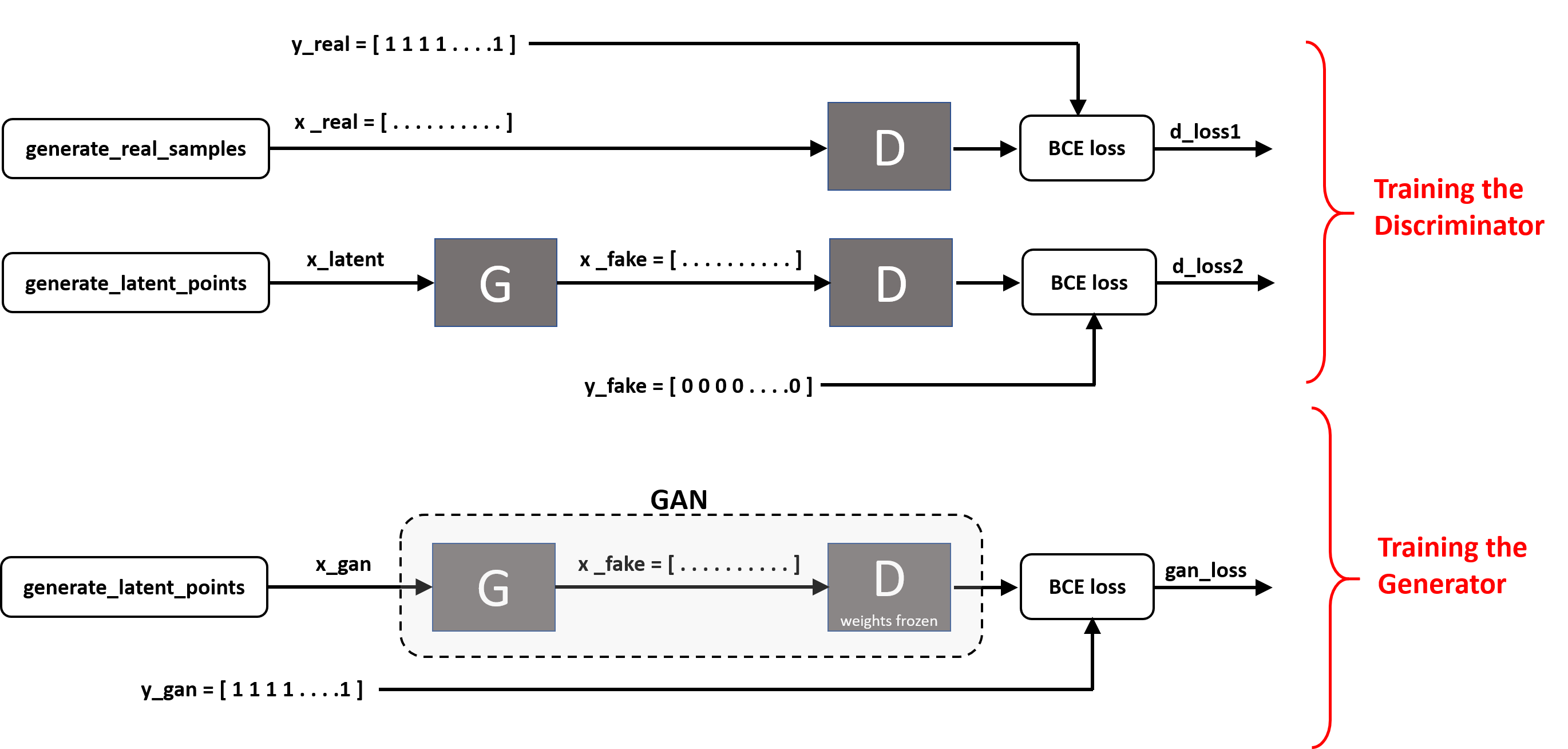
Training process diagram
 |
n_epochs=30000
n_batch=128
n_eval=6000
# determine half the size of one batch, for updating the discriminator
half_batch = int(n_batch / 2)
# manually enumerate epochs
for i in range(n_epochs):
# prepare real samples
x_real, y_real = generate_real_samples(half_batch)
# prepare fake examples
# generate points in latent space and pass them through generator to generate fake examples.
x_latent = generate_latent_points(latent_dim, half_batch)
x_fake = generator_model.predict(x_latent)
# create class labels
y_fake = zeros((half_batch, 1))
# update discriminator
d_loss1, d_acc1 = discriminator_model.train_on_batch(x_real, y_real)
d_loss2, d_acc2 = discriminator_model.train_on_batch(x_fake, y_fake)
# prepare points in latent space as input for the generator
x_gan = generate_latent_points(latent_dim, n_batch)
# create inverted labels for the fake samples
y_gan = ones((n_batch, 1))
# update the generator via the discriminator's error
gan_loss = gan_model.train_on_batch(x_gan, y_gan)
# evaluate the model every n_eval epochs
if (i+1) % n_eval == 0:
print('epoch:%d, d1[%.3f] d2[%.3f] g[%.3f]' % (i+1, d_loss1, d_loss2, gan_loss))
evaluate(i, generator_model, discriminator_model, latent_dim)
/src/keras/engine/training.py:490: UserWarning: Discrepancy between trainable weights and collected trainable weights, did you set `model.trainable` without calling `model.compile` after ?
'Discrepancy between trainable weights and collected trainable'
epoch:6000, d1[0.691] d2[0.692] g[0.693]
5999 0.33 0.63
epoch:12000, d1[0.685] d2[0.698] g[0.687]
11999 0.56 0.69
epoch:18000, d1[0.692] d2[0.690] g[0.697]
17999 0.41 0.63
epoch:24000, d1[0.689] d2[0.693] g[0.694]
23999 0.77 0.45
epoch:30000, d1[0.704] d2[0.682] g[0.700]
29999 0.5 0.49